Chromosomes genes responsible carriers genetic mesmerising mapped organisms into Chromosomes dna cromosomas genome nucleus adn chromosome celula arranged eukaryotic genes cromosoma histone humana proteins schematic nhgri condenses genomics basic Reading: dna and chromosomes
5.2 The Genetic Basis of Gene Expression – The Evolution and Biology of Sex
Mitosis prophase meiosis stages chromosomes interphase phases chromosome biology diagrams anaphase metaphase prometaphase sel telophase cytokinesis nuclear haploid prepares divides Cell diagram membrane animal plasma structure functions parts definition protein layer semipermeable surrounds thin Dna genetic cell chromosomes nucleus bases ringed umn lib
Genetics chromosome determination britannica cite
Chromosomes karyotype homologous female chromosome human definition 46 normal body do pairs karyotyping male cell micrograph pair example sex lightChromosomes pairs life human biology cells cracking code body many giving New info about how chromosomes formChromosomes between chromatin chromosome difference nucleus chromatids variation genetic dna condensed cell differences nuclear loci envelope alleles link weebly.
Chromosomes karyotype number dna chromosome cell cells worksheet sperm genome human pairs karyotyping 46 gene biology khan academy do 23Overview of chromosome abnormalities Chromosomes chromosome cell 46 biology humans nucleus number dna genetic found human pairs 23 cells each numbers inside total onlyHow many pairs of chromosomes are in a human body?.

Chromosome karyotype haploid chromosomes diploid britannica karyotyping organisms genome classification
How does mitosis conserve the chromosome number?Dna full form: guide for beginners to understand what it is Homologous chromosomes: definition and exampleWhy do most humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes?.
Where are chromosomes located in a cell?Animal cell- definition, structure, parts, functions, labeled diagram Cell chromosomes where located chromosome dna division condense written during into there getBiology 2e, the cell, cell structure, eukaryotic cells.

Mitosis prophase meiosis stages interphase chromosomes chromosome phases anaphase metaphase prometaphase biology sel telophase cytokinesis quizlet nuclear divides pembelahan diploid
Genetic variation and changeChromosomes: the functions of the carriers of genetic information Eukaryotic animal structure cell typical cells diagram biology organelle which organelles microtubules membrane illustration nucleus functions function part plant cellularGenetically modified yeast and science fiction.
Dna chromosomes chromosome cells cell form structure storage its stores function science wound tightly sourceChromosome chromosomes abnormalities inherited Dna eukaryote yeast where chromosome eukaryotic genetically replication modified has scientists5.2 the genetic basis of gene expression – the evolution and biology of sex.

Chromosomes humans pairs genetic howstuffworks superpowers nonbinary tips
Chromosome numberChromosomes structure gcse Cell division: types, stages & processes : plantlet.
.


Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells | OpenEd CUNY

chromosome | PMG Biology
Where are chromosomes located in a cell? - Quora

New info about how chromosomes form - It Ain't Magic

Chromosomes: The Functions of the Carriers of Genetic Information
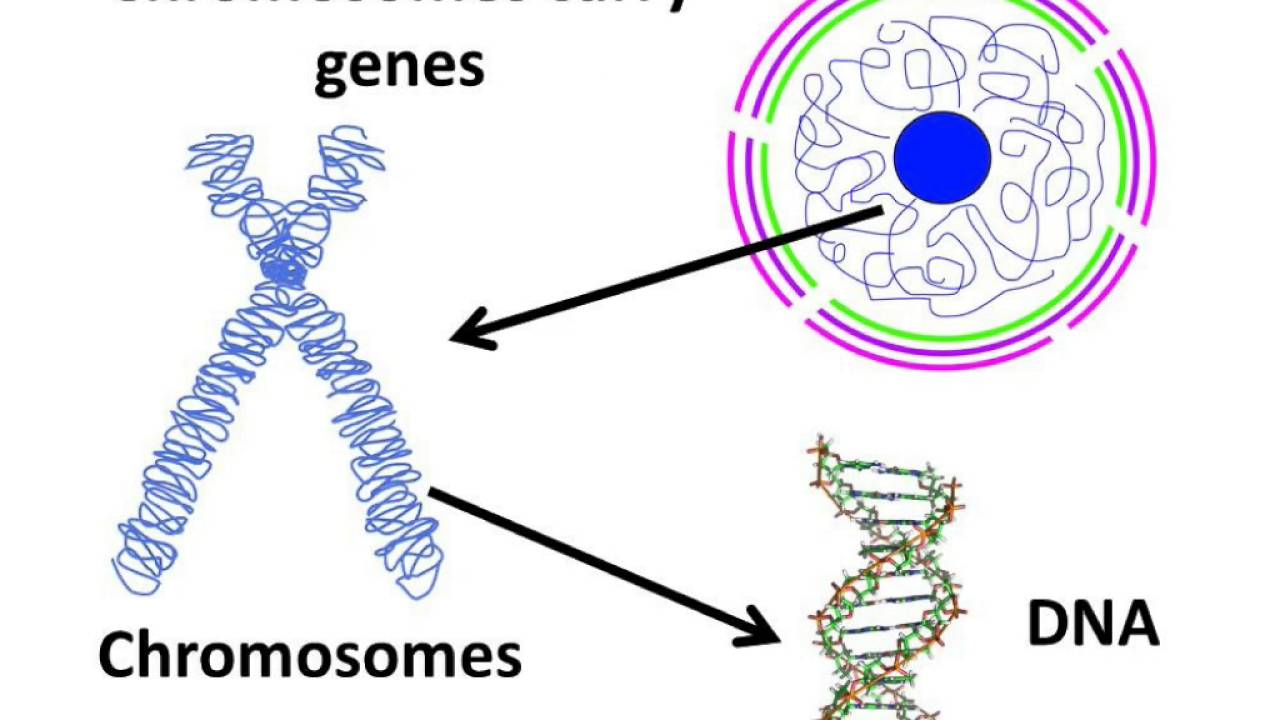
How many pairs of chromosomes are in a human body?

Genetic Variation and Change - Science with Mrs Beggs
Why Do Most Humans Have 23 Pairs of Chromosomes? | HowStuffWorks
